Due to poor sealing of the assembly sleeve, moisture enters the interior, reducing the insulation resistance; or the oil level drops due to oil leakage, resulting in pole-to-shell discharge or component breakdown. Power capacitor bulging and internal dissociation: due to the internal generation of corona, breakdown discharge and internal dissociation, the initial dissociation voltage of the capacitor is reduced to below the working electric field strength under the action of overvoltage, which causes physical, chemical and electrical damage. Effect, accelerate the aging and decomposition of the insulation, generate gas, form a vicious circle, increase the pressure of the box shell, cause the box wall to bulge and explode. Closing with charge causes explosion of power capacitors: Capacitor banks with any rated voltage are prohibited from closing with charge.
Every time the capacitor bank is re-closed, the capacitor must be discharged for 3 minutes after the switch is turned off, otherwise the capacitor will explode due to the residual charge on the capacitor at the moment of closing. For this reason, it is generally stipulated that capacitor banks with a capacity of more than 160 kvar should be equipped with an automatic discharge device when there is no voltage, and it is stipulated that the switch of the capacitor bank is not allowed to be equipped with automatic closing. In addition, power capacitors may be damaged and exploded due to excessive temperature, poor ventilation, excessive operating voltage, excessive harmonic components, or operating overvoltage.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى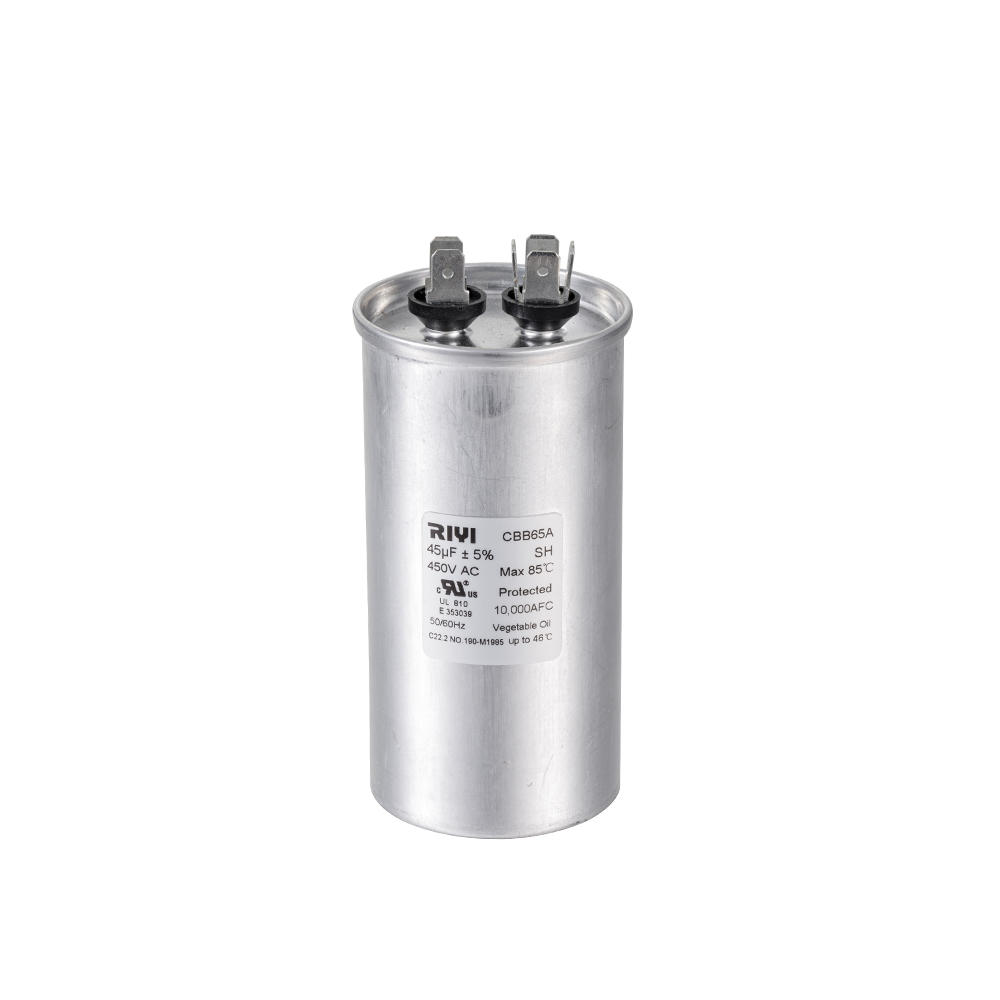
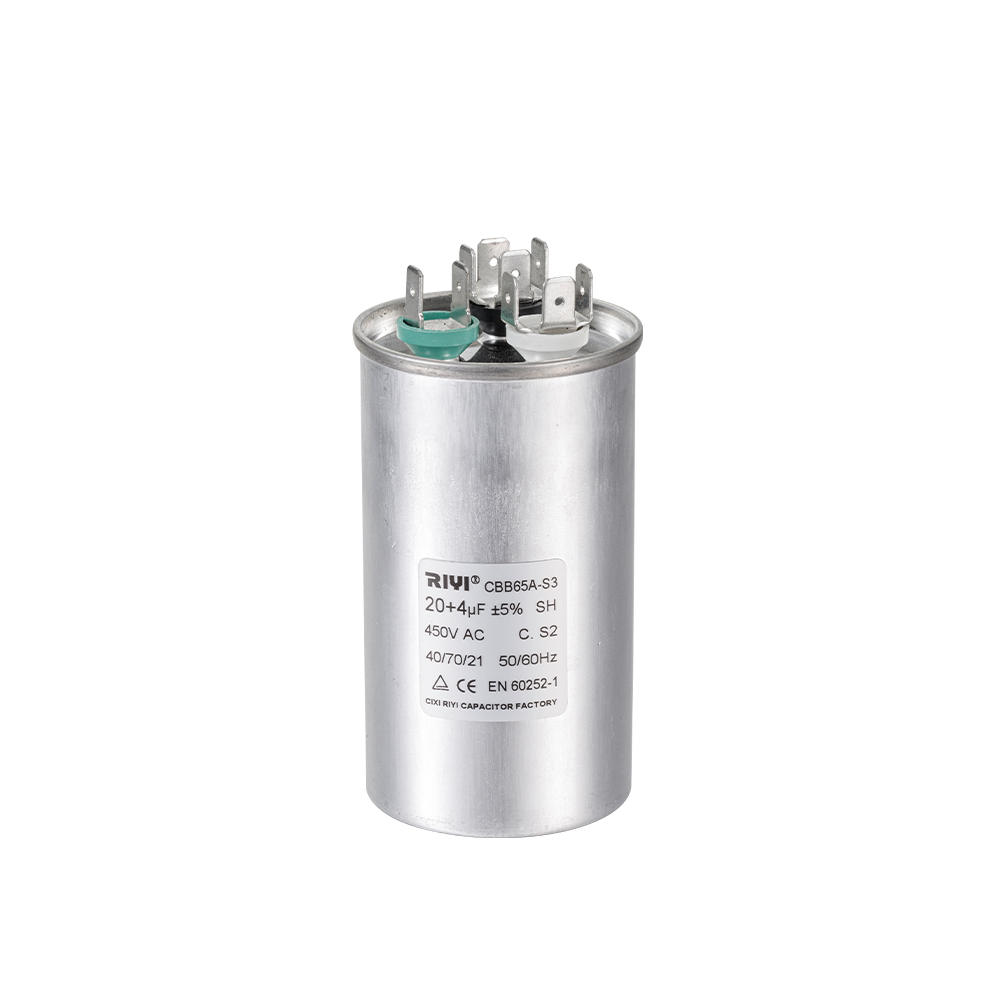
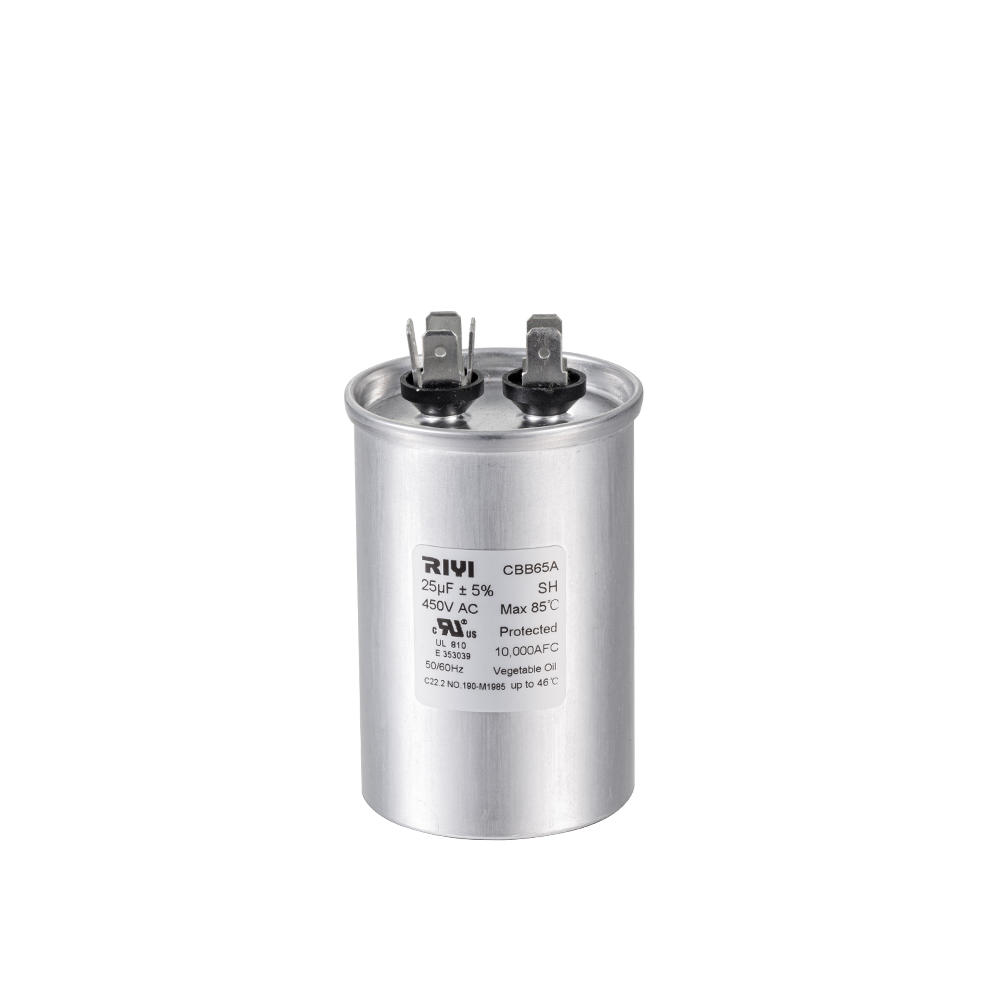
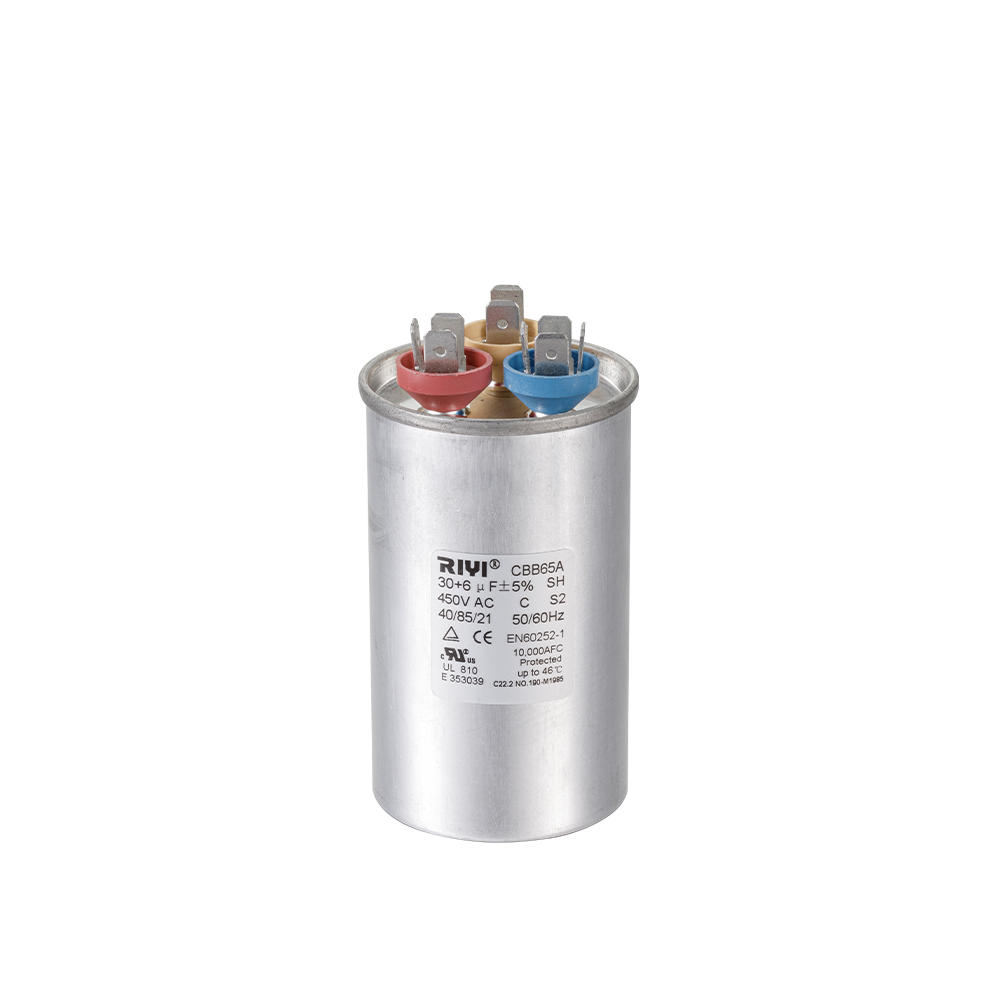
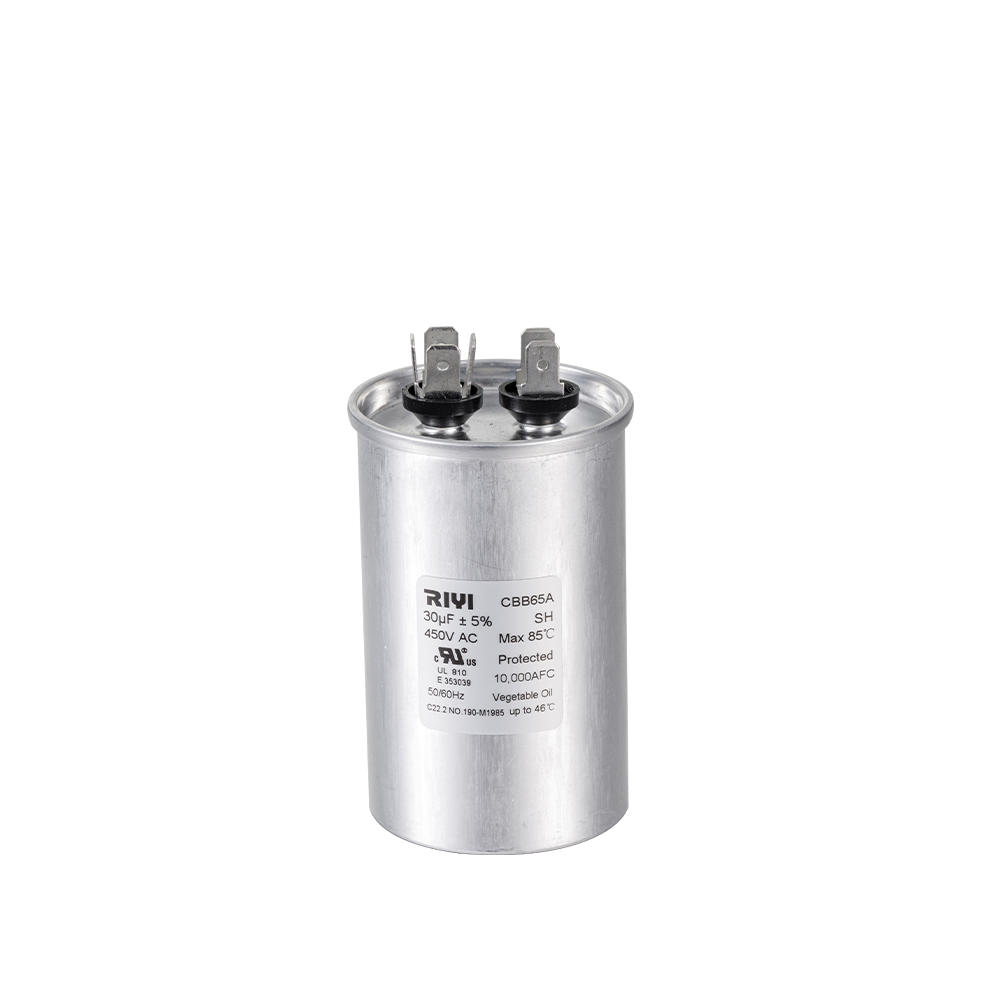











 +86-13600614158
+86-13600614158
 +86-0574-63223385
+86-0574-63223385 Zonghan Street,Cixi City,Zhejiang Province,China.
Zonghan Street,Cixi City,Zhejiang Province,China.