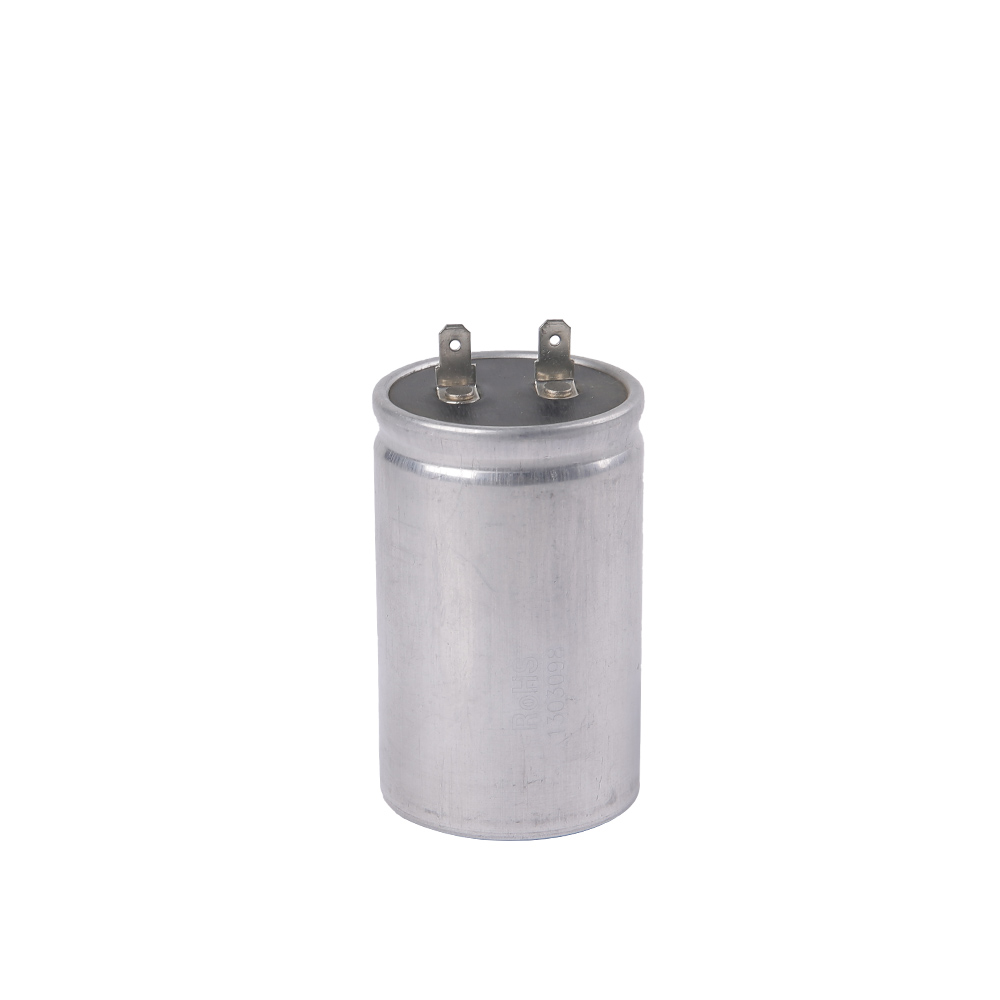
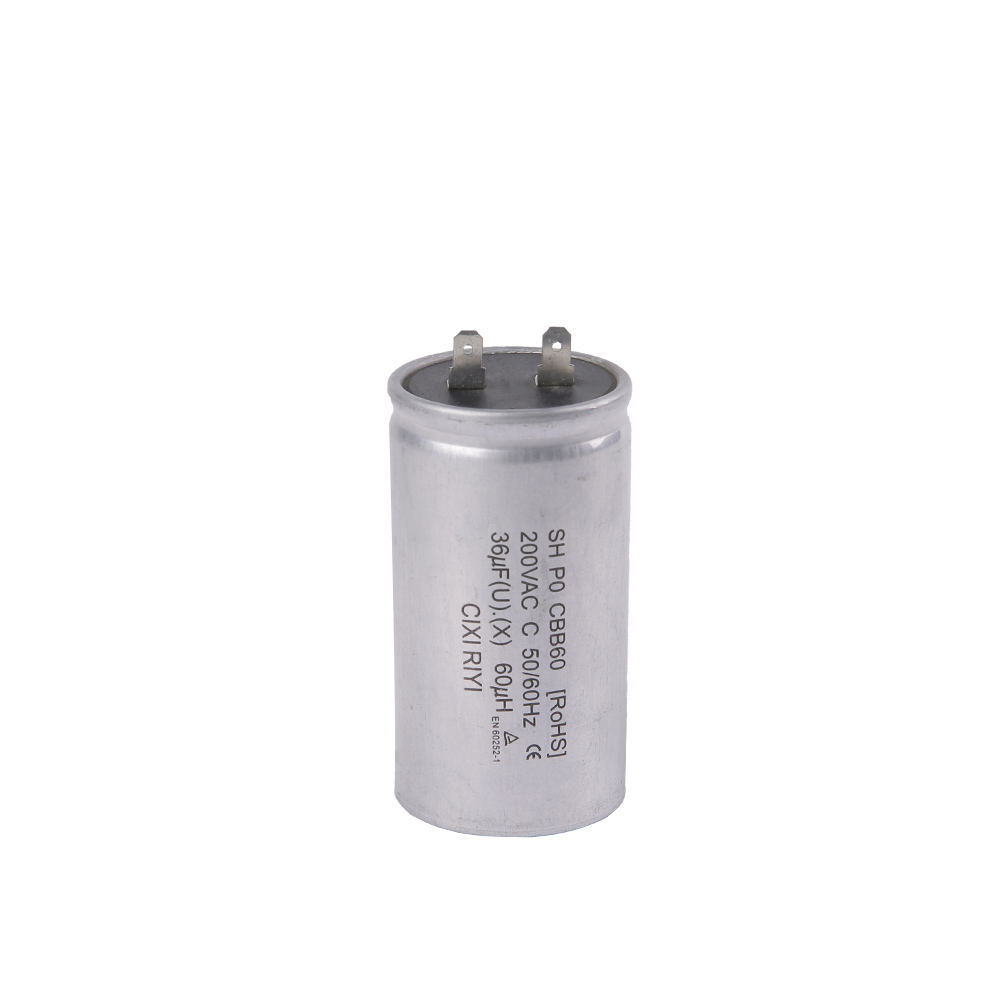
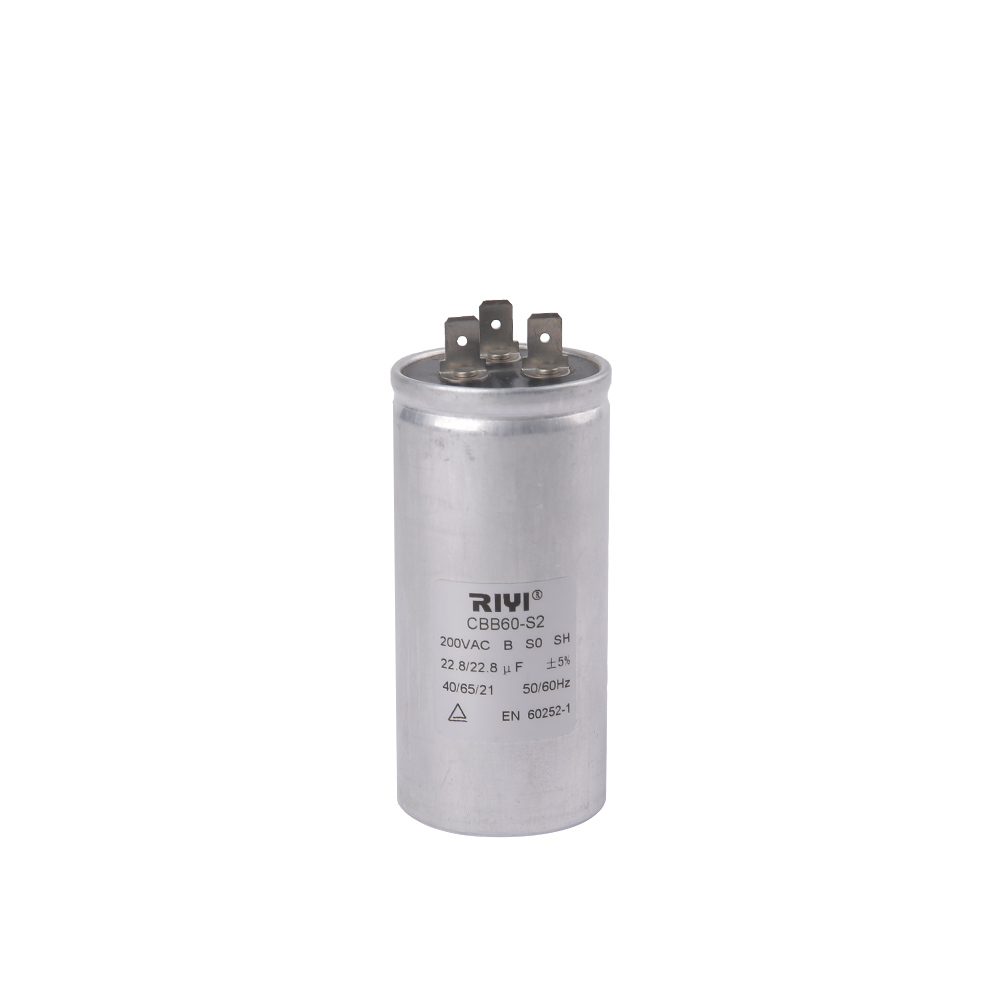
The size and package of an AC capacitor refer to its physical dimensions and the way it is constructed, housed, and mounted. The size and package of an AC capacitor can vary significantly depending on its intended application and voltage rating. Here is an introduction to AC capacitor size and package considerations:
1.Physical Size: AC capacitors come in various physical sizes, ranging from small surface-mount capacitors used in electronic circuits to larger cylindrical or rectangular capacitors used in industrial applications. The physical size is determined by factors such as the capacitor's capacitance, voltage rating, and construction.
2.Capacitance: Capacitance value affects the size of a capacitor. Higher capacitance values often require larger physical dimensions. For example, a capacitor with a capacitance of 1 microfarad (µF) is typically much smaller than a capacitor with a capacitance of 1 farad (F).
3.Voltage Rating: The voltage rating of a capacitor also influences its size. Capacitors designed for higher voltage applications typically have larger physical dimensions to accommodate the required insulation and dielectric material thickness.
4.Mounting Style: AC capacitors can be mounted in various ways, depending on the application. Common mounting styles include:
Through-Hole Mounting: This involves inserting capacitor leads through holes in a circuit board and soldering them in place. It is common for small electronic capacitors.
Surface-Mount Technology (SMT): Surface-mount capacitors are soldered directly onto the surface of a circuit board, eliminating the need for leads.
Bolted or Screw Mounting: Larger capacitors used in industrial applications often have mounting holes or brackets for secure attachment to equipment or panels.
5.Termination Type: The way the leads or terminals of a capacitor are designed can vary. Common termination types include radial leads (axial leads), axial leads, snap-in terminals, lug terminals, and wire leads. The choice of termination type depends on how the capacitor will be connected in the circuit.
6.Enclosure or Case: Capacitors are often enclosed in protective cases or housings. The material and design of the enclosure can vary depending on factors such as the environment in which the capacitor will operate and safety requirements. For example, plastic or metal cases may be used.
7.Cooling: In high-power or high-frequency applications, capacitors may have cooling fins or other features to dissipate heat and maintain optimal performance.
8.Labels and Markings: AC capacitors typically have labels or markings that provide information about their specifications, including capacitance, voltage rating, temperature ratings, manufacturer information, and safety certifications.
9.Safety Features: Some capacitors include safety features such as pressure-sensitive interrupters or discharge resistors to enhance safety and prevent electrical shock hazards.
When selecting an AC capacitor, it's crucial to consider the size and package to ensure that it fits within the available space, is compatible with the mounting method, and meets the requirements of the intended application. Consulting the capacitor datasheet and manufacturer's guidelines is essential to make the right choice.
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى











 +86-13600614158
+86-13600614158 mina@cxriyi.com
mina@cxriyi.com +86-0574-63223385
+86-0574-63223385 Zonghan Street,Cixi City,Zhejiang Province,China.
Zonghan Street,Cixi City,Zhejiang Province,China.